which of the following is not a biomass energy source
Advantages And Disadvantages of Biomass Energy

Question 1: What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is a renewable source of energy that is derived from organic materials, such as plants and animal waste. It involves using these organic materials to generate heat, electricity, or fuel.
Question 2: What are the advantages of biomass energy?
Advantages of biomass energy include:
- Renewable and sustainable source of energy
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Utilizes organic waste material
- Creates job opportunities in the biomass industry
Question 3: Are there any disadvantages of biomass energy?
Disadvantages of biomass energy include:
- High production costs
- Potential for deforestation if unsustainable practices are followed
- Emission of air pollutants during combustion
- Requirement of large land areas for biomass cultivation
Question 4: How is biomass energy generated?
Biomass energy can be generated through processes like combustion, gasification, anaerobic digestion, and pyrolysis.
Combustion involves burning biomass to produce heat, which can then be converted into electrical or mechanical energy.
Gasification involves heating biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce a combination of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane gases. These gases can then be used to generate electricity.
Anaerobic digestion involves the breakdown of organic materials by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. This process produces biogas, which can be used as a source of energy.
Pyrolysis involves heating biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce liquid bio-oil, syngas, and biochar. These products can be used for energy purposes.
Question 5: Can biomass energy be used for heating purposes?
Yes, biomass energy can be used for heating purposes. Biomass boilers and stoves are commonly used to provide heat in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. These systems burn biomass to produce hot water, steam, or air, which can then be used for heating buildings or other applications.
Question 6: Is biomass energy a sustainable source of energy?
Yes, biomass energy is considered a sustainable source of energy. It relies on organic materials that can be replenished through natural processes, such as the growth of plants. However, it is important to ensure sustainable practices in biomass production and harvest to avoid depleting natural resources or causing environmental harm.
Question 7: Does biomass energy contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Yes, biomass energy can contribute to reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. When organic materials are burned or processed to generate energy, the carbon dioxide released is considered part of the natural carbon cycle. As long as the biomass is derived from sustainably managed sources, it results in a carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative energy source, as the carbon dioxide emitted is offset by the carbon absorbed by plants during photosynthesis.
Question 8: Can biomass energy help in waste management?
Yes, biomass energy can help in waste management. It provides a way to utilize organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues, forest residues, or food waste, which might otherwise be disposed of in landfills. By converting these waste materials into energy, biomass energy helps reduce the volume of waste, minimize methane emissions from landfills, and contribute to a circular economy.
Question 9: Who can benefit from biomass energy?
Various stakeholders can benefit from biomass energy:
- Households and businesses can use biomass energy for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
- Farmers and landowners can generate additional income by producing biomass feedstocks for energy production.
- Communities located near biomass power plants can benefit from job creation and economic development.
- Environmentally conscious individuals and organizations can support the transition to renewable energy and contribute to mitigating climate change.
Question 10: What are some challenges associated with biomass energy?
Challenges associated with biomass energy include:
- Ensuring sustainable biomass production and harvest practices
- Addressing potential negative impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems
- Dealing with the logistics of biomass collection, storage, and transportation
- Improving the efficiency of biomass conversion technologies
- Ensuring air quality standards are met during biomass combustion
Question 11: Can biomass energy replace fossil fuel-based energy sources?
Biomass energy has the potential to replace a portion of fossil fuel-based energy sources. However, it is unlikely to completely replace them due to the limitations in biomass availability and the need for a diverse portfolio of renewable energy sources. Biomass energy can play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a more sustainable energy mix.
Question 12: Are there any governmental incentives or policies supporting biomass energy?
Many governments around the world have implemented incentives and policies to support biomass energy:
- Feed-in tariffs: Provide financial incentives for the production of renewable energy, including biomass.
- Tax credits: Offer tax benefits to individuals or businesses investing in biomass energy projects.
- Renewable portfolio standards: Require a certain percentage of energy to come from renewable sources, including biomass.
- Grants and subsidies: Provide funding to support the development and implementation of biomass energy projects.
Advantages of Biogas
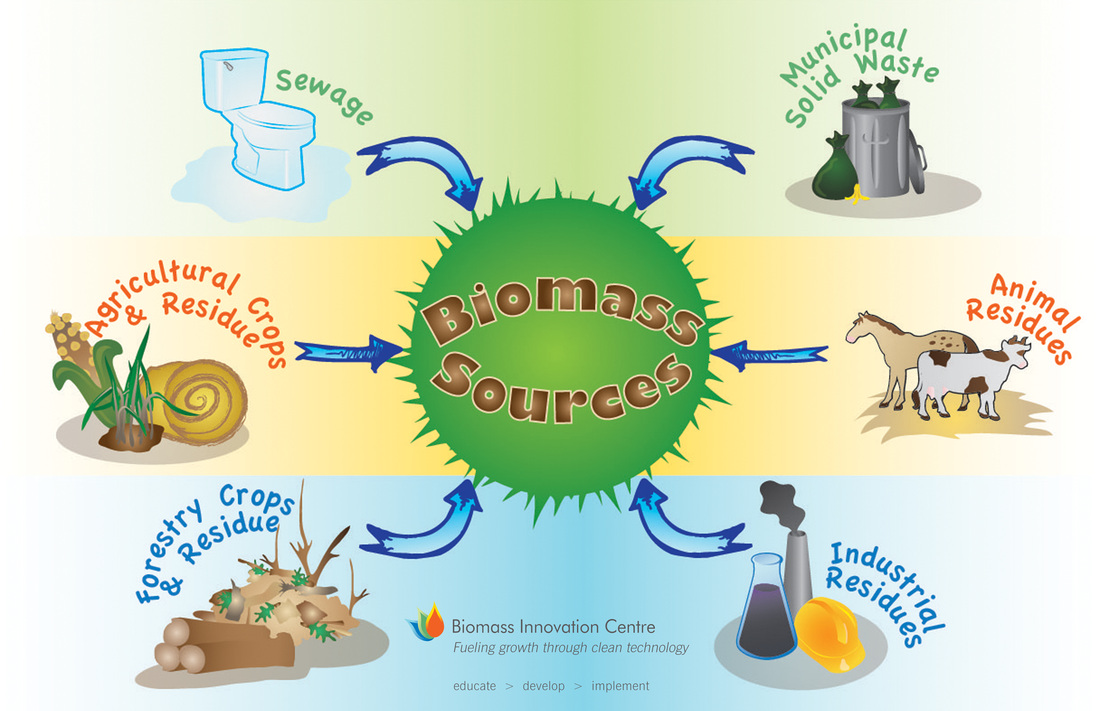
Question 1: What is biogas?
Biogas is a renewable source of energy that is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials, such as animal manure, agricultural residues, and food waste. It is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane and carbon dioxide.
Question 2: What are the advantages of biogas?
Advantages of biogas include:
- Renewable and sustainable source of energy
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Provides a method for waste management
- Can be used for various applications like cooking, heating, and electricity generation
- Can be produced locally, reducing dependence on external energy sources
Question 3: How is biogas produced?
Biogas is produced through a process called anaerobic digestion. In this process, organic materials are broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. The bacteria convert the organic matter into biogas, which consists primarily of methane (50-70%) and carbon dioxide (30-50%), along with small amounts of other gases.
Question 4: Can biogas be used for cooking?
Yes, biogas can be used for cooking purposes. Biogas stoves and burners are commonly used in households, particularly in rural areas, where access to clean cooking fuels may be limited. The combustion of biogas produces a clean and efficient flame, providing a viable alternative to traditional cooking fuels like wood or charcoal.
Question 5: How can biogas contribute to sustainable agriculture?
Biogas can contribute to sustainable agriculture in several ways:
- Utilization of animal manure: Biogas production allows farmers to efficiently manage animal waste, reducing odor, pathogens, and greenhouse gas emissions while producing renewable energy.
- Nutrient recycling: The digestate produced as a byproduct of biogas production can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer for crops, reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
- Improved soil health: The application of digestate can enhance soil fertility, organic matter content, and microbial activity, leading to improved soil health and crop productivity.
Question 6: Can biogas be used for electricity generation?
Yes, biogas can be used for electricity generation. Biogas can be combusted in an engine or a turbine to produce mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity through a generator. This process, known as cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP), allows for the simultaneous production of electricity and heat.
Question 7: Is the production of biogas environmentally friendly?
The production of biogas is considered environmentally friendly due to several reasons:
- Reduces methane emissions: Anaerobic digestion of organic materials prevents the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels: The use of biogas as a renewable energy source reduces the need for fossil fuel-based energy sources, thereby contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste management: Biogas production provides a sustainable solution for managing organic waste materials, reducing their environmental impact and potential pollution.
Question 8: Can biogas be stored for future use?
Yes, biogas can be stored for future use. Biogas can be compressed and stored in gas storage tanks or converted into other forms, such as biomethane, which can be injected into the natural gas grid. Storing biogas allows for its use during periods of high energy demand or when the primary source of biogas production is not available.
Question 9: Are there any challenges associated with biogas production?
Challenges associated with biogas production include:
- Availability of feedstock: Sufficient quantities of organic materials are required to ensure continuous biogas production, which can be a challenge in certain regions or during specific seasons.
- Feedstock composition: The composition of organic materials used as feedstock can affect the efficiency and stability of biogas production. Balancing the feedstock inputs and maintaining optimal conditions for anaerobic digestion is essential.
- Technological requirements: Biogas production requires appropriate anaerobic digestion systems and gas handling equipment, which may require upfront investments and skilled operation.
Question 10: Can biogas be used as a transportation fuel?
Yes, biogas can be upgraded to biomethane, which has similar properties to natural gas. Biomethane can be used as a transportation fuel in compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG) vehicles. The utilization of biomethane as a transportation fuel can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Question 11: Are there any incentives or policies supporting biogas production?
Many countries have implemented incentives and policies to support biogas production:
- Feed-in tariffs: Offer favorable electricity prices for biogas producers, encouraging the injection of biogas into the grid.
- Renewable energy incentives: Provide financial support or tax benefits to promote the development of biogas projects.
- Bioenergy strategies: Governments establish strategies and targets for the development and utilization of renewable energy, including biogas.
Question 12: Can biogas production benefit local communities?
Yes, biogas production can benefit local communities in several ways:
- Energy independence: Local production of biogas reduces the dependence on external energy sources, enhancing energy security and resilience.
- Job creation: Biogas projects require technicians, operators, and maintenance personnel, generating employment opportunities in the local community.
- Waste management: Biogas production provides a sustainable solution for managing organic waste, reducing its environmental impact and potential health risks.
Overall Article: Biomass Energy and Biogas - Renewable Energy Solutions
Biomass energy and biogas are two renewable energy sources that offer numerous advantages in the transition towards sustainable energy systems. Both biomass energy and biogas utilization contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting waste management, and providing alternative sources of energy for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
Biomass energy involves the utilization of organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, to produce heat, electricity, or fuel. It offers advantages such as being a renewable and sustainable energy source, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and utilizing organic waste materials. However, it also has some disadvantages, including high production costs and potential environmental impacts.
Biogas, on the other hand, is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials like animal manure, agricultural residues, and food waste. It represents a renewable source of energy that can be used for cooking, heating, and electricity generation. Biogas production offers advantages such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, providing a method for waste management, and supporting sustainable agriculture. However, it also faces challenges related to feedstock availability and technological requirements.
Both biomass energy and biogas have the potential to contribute significantly to a more sustainable energy mix. Governments worldwide have implemented various incentives and policies to support their production and utilization. Feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and renewable portfolio standards are some of the measures aimed at promoting the growth of biomass and biogas projects.
In conclusion, biomass energy and biogas offer renewable alternatives to traditional energy sources. They provide opportunities for waste management, stimulate economic growth through job creation, and contribute to mitigating climate change. As the world continues to prioritize sustainable development, the utilization of biomass energy and biogas will play a crucial role in achieving cleaner and more resilient energy systems.