which example is not a biomass energy source
Advantages of Biogas
Biogas is a renewable energy source that offers various advantages for both the environment and individuals. Here are some commonly asked questions about the advantages of biogas:
1. What is biogas?
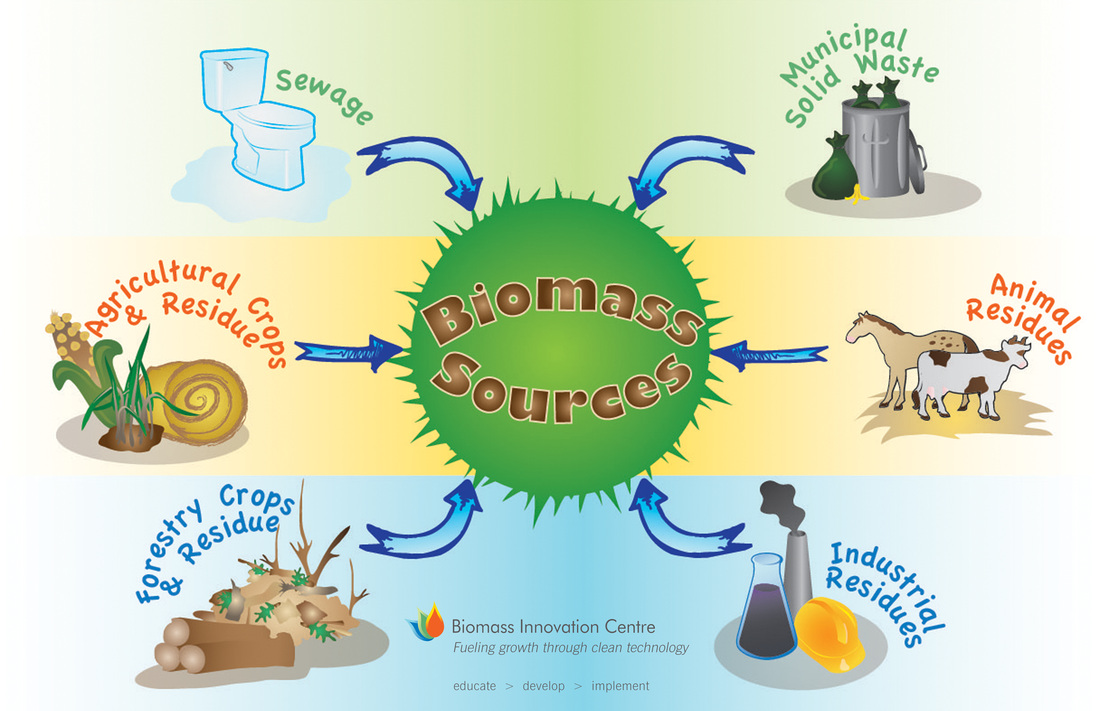 Biogas is a type of renewable energy that is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion. It is primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gases, along with small amounts of other gases. Biogas can be generated from organic materials such as agricultural waste, sewage, and organic household waste.
Biogas is a type of renewable energy that is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion. It is primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gases, along with small amounts of other gases. Biogas can be generated from organic materials such as agricultural waste, sewage, and organic household waste.
- Comprised mostly of methane, a potent greenhouse gas
- Produced through anaerobic digestion of organic materials
- Highly versatile and can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a vehicle fuel
2. What are the advantages of biogas?
Biogas offers several advantages over other forms of energy:
- Renewable: Biogas is a renewable energy source, as it is derived from organic materials that can be continuously produced.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: As biogas is primarily composed of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, its capture and utilization helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Management: Biogas production provides a sustainable way to manage organic waste, such as agricultural residues and sewage, by converting it into a valuable energy resource.
- Energy Independence: Biogas can contribute to energy independence by providing a decentralized and locally available source of energy.
- High Energy Efficiency: Biogas can be efficiently converted into heat, electricity, and even upgraded to biomethane for use as a vehicle fuel.
- Improved Soil Health: The byproduct of biogas production, known as digestate, is a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer that can enhance soil fertility and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
3. How is biogas produced?
Biogas is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion. Organic materials, such as agricultural waste, sewage, and organic household waste, are broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of biogas.
- Raw materials, such as food waste or animal manure, are collected and stored in an anaerobic digester.
- The anaerobic digester creates the ideal conditions for bacteria to break down the organic materials and produce biogas.
- The biogas is then captured and can be used for various applications.
- The remaining residue, known as digestate, can be used as an organic fertilizer.
4. Can biogas be used for electricity generation?
 Yes, biogas can be used as a fuel for electricity generation. Biogas power plants utilize the combustion of biogas to produce electricity. The process involves:
Yes, biogas can be used as a fuel for electricity generation. Biogas power plants utilize the combustion of biogas to produce electricity. The process involves:
- Biogas being burned in an engine or a turbine to generate mechanical energy.
- The mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy through the use of a generator.
- The generated electricity can be used to power homes, businesses, or be fed into the grid.
Biogas power plants contribute to sustainable energy production as they utilize a renewable resource and emit fewer greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuel power plants.
5. Is biogas a suitable replacement for traditional fuels?
Biogas can serve as a suitable replacement for traditional fuels in certain applications, but it may not be viable for all purposes. Here are some considerations:
- Cooking and Heating: Biogas can be used as an alternative to fossil fuels for cooking and heating in households and industries. It provides a cleaner-burning and renewable option.
- Vehicle Fuel: Biogas can be upgraded to biomethane and used as a vehicle fuel. However, the availability of infrastructure and vehicles compatible with biogas can be limiting factors.
- Electricity Generation: Biogas can efficiently generate electricity, but other renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy may be more suitable for large-scale power generation.
While biogas has its advantages, the suitability of its use depends on factors such as availability of feedstock, infrastructure, and local energy requirements.
Is Biomass Renewable?
Biomass, as a source of energy, has gained attention due to its potential as a renewable resource. Here are some commonly asked questions about the renewability of biomass:
1. What is biomass?
 Biomass refers to organic matter derived from plants, animals, and other organic sources that can be used as a source of energy. It includes agricultural residues, wood pellets, energy crops, and organic waste materials.
Biomass refers to organic matter derived from plants, animals, and other organic sources that can be used as a source of energy. It includes agricultural residues, wood pellets, energy crops, and organic waste materials.
- Biomass can be used directly as fuel or converted into various forms of bioenergy, such as biogas, bioethanol, and biodiesel.
- It is considered a renewable resource as it can be continually replenished through sustainable management practices.
2. Is biomass considered a renewable energy source?
Yes, biomass is generally considered a renewable energy source. The renewability of biomass depends on sustainable practices, such as:
- Utilizing biomass from sustainably managed forests and plantations, where new trees are planted to replace those used for energy production.
- Using agricultural residues and organic waste materials that would otherwise decompose and release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Growing energy crops, such as miscanthus or switchgrass, on dedicated land without impacting food production or biodiversity.
These practices ensure that biomass is harvested in a way that allows for regrowth or prevents the release of additional carbon dioxide emissions.
3. How is biomass used as a renewable energy source?
Biomass can be utilized as a renewable energy source through various processes, including:
- Direct Combustion: Biomass is burned directly to generate heat energy, commonly used for heating purposes in residential and industrial settings.
- Biogas Production: Organic materials, such as agricultural waste and organic household waste, can undergo anaerobic digestion to produce biogas. This biogas can be used for heating, electricity production, or as a vehicle fuel.
- Bioethanol Production: Biomass, particularly sugarcane and corn, can be fermented to produce bioethanol, which is commonly blended with gasoline or used as a standalone fuel for transportation.
- Biodiesel Production: Certain plants, such as soybeans or rapeseed, can be processed to extract oils that are then converted into biodiesel, a renewable alternative to fossil diesel.
- Pyrolysis and Gasification: Biomass can undergo thermal processes like pyrolysis and gasification to produce bio-oil, syngas, or charcoal, which can be further utilized for heat, electricity, or biofuel production.
These processes allow for the utilization of biomass as a renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
4. What are the environmental benefits of biomass as a renewable energy source?
Biomass offers several environmental benefits, including:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Using biomass for energy production reduces the net carbon emissions compared to fossil fuel combustion. This is because the carbon dioxide released during biomass combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during growth.
- Waste Reduction: Utilizing agricultural residues and organic waste materials as biomass feedstock helps in diverting these materials from landfills, reducing methane emissions and promoting sustainable waste management.
- Improved Soil Health: Biomass residues, such as crop residues or manure, can be used as organic fertilizers, enhancing soil fertility and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Renewable Energy Generation: Biomass provides a locally available and renewable source of energy, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels and contributing to energy security.
These environmental benefits make biomass an attractive option for transitioning to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy system.
5. Can biomass be used for large-scale electricity generation?
 Yes, biomass can be utilized for large-scale electricity generation through dedicated power plants. Some key points to consider:
Yes, biomass can be utilized for large-scale electricity generation through dedicated power plants. Some key points to consider:
- Dedicated biomass power plants typically utilize technologies like fluidized bed combustion or biomass gasification.
- Biomass is fed into a boiler where it is combusted to generate high-pressure steam.
- The steam drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- The generated electricity can be distributed through the grid to power homes, businesses, and industries.
Biomass power plants can play a significant role in providing baseload renewable electricity, especially in regions with ample biomass resources.