what is the definition of biomass energy
What Is Biomass Energy? Biomass Definition, Examples & Process | Inspire

Biomass energy refers to the energy that is derived from organic matter, such as plants, animal waste, and other types of biological material. It is a renewable energy source that can be used to generate electricity, heat, or fuel for transportation.
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about biomass energy:
What are the different types of biomass?
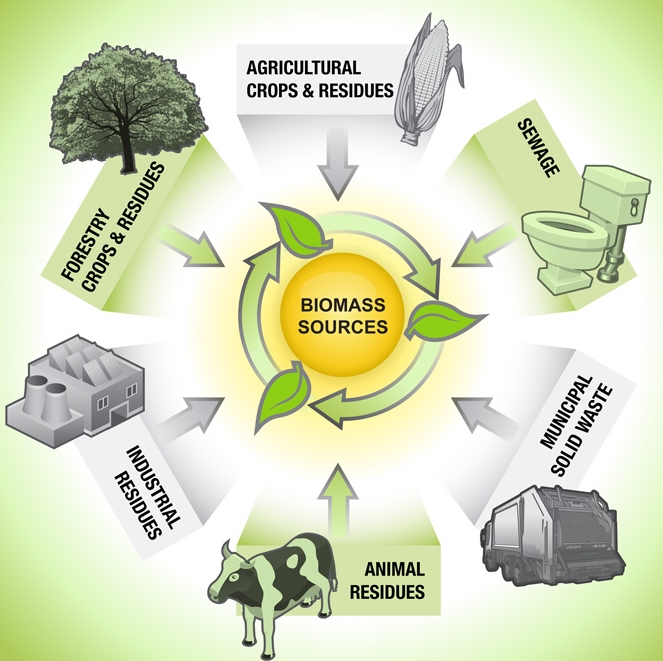
Biomass can come from various sources, including:
- Forest residues, such as branches and tree stumps
- Agricultural residues, like corn stalks and rice husks
- Animal waste, such as manure
- Energy crops, like corn and sugarcane
- Wood pellets and other forms of processed biomass
Each type of biomass has unique characteristics and can be utilized for different purposes.
How is biomass converted into energy?
Biomass can be converted into energy through various processes, including:
- Combustion: Biomass is burned to produce heat, which can then be used to generate electricity or directly for heating.
- Gasification: Biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce a gas mixture called syngas. Syngas can be used to power engines or turbines.
- Anaerobic digestion: Biomass is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas. Biogas can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a renewable natural gas.
- Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen to produce bio-oil, biochar, and gases. Bio-oil can be further processed into transportation fuels.
What are the advantages of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several advantages:
- Renewable: Biomass is derived from organic sources that can be replenished.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy produces lower levels of greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels.
- Waste management: Biomass utilization helps in the management and disposal of agricultural and forestry waste.
- Local economic development: Biomass energy production can create jobs and support local economies.
Are there any challenges associated with biomass energy?
Despite its benefits, biomass energy also faces some challenges:
- Resource availability: Availability and collection of biomass can be influenced by weather conditions and geographical factors.
- High capital costs: Building biomass power plants and related infrastructure can require significant investment.
- Competing land use: The cultivation of energy crops for biomass production can compete with food crops or natural habitats.
- Emissions: Some biomass combustion processes can emit pollutants, although modern technologies are improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
Is biomass energy sustainable?
Biomass energy can be considered sustainable if certain conditions are met:
- Regulated harvesting: Biomass should be harvested in a sustainable manner, ensuring the long-term health of forests and ecosystems.
- Efficient use: Biomass should be utilized efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing energy output.
- Carbon neutrality: The carbon emissions from biomass combustion should be offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of new biomass.
- Environmental considerations: The environmental impacts of biomass production and utilization should be carefully assessed and mitigated.
How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources?
Biomass energy has its own advantages and disadvantages when compared to other renewable energy sources:
- Advantages:
- It can provide a constant and reliable source of electricity, unlike some intermittent renewables like solar or wind power.
- It can utilize existing infrastructure designed for fossil fuels, making it easier to transition to biomass energy.
- It can support local economies and provide job opportunities in rural areas.
- Disadvantages:
- It requires a continuous supply of biomass, which may have limitations in terms of resource availability.
- It can produce emissions and pollutants, although modern technologies are working to minimize these impacts.
- Compared to other renewables like solar or wind power, it may have higher capital and operating costs.
What is the impact of biomass energy on climate change?
Biomass energy can contribute to mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions:
- Carbon neutrality: Biomass fuels, when produced sustainably, can be considered carbon-neutral since the carbon emitted during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of new biomass.
- Replacement of fossil fuels: Biomass energy can replace fossil fuels in electricity generation and heating, reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste management: Utilizing agricultural and forestry waste for energy production reduces methane emissions from decomposition and provides an alternative to open burning.
What policies support the development of biomass energy?
Several policies and incentives exist to support the development of biomass energy:
- Renewable portfolio standards: These policies require utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources, including biomass.
- Feed-in tariffs: Governments can offer feed-in tariffs, providing guaranteed payments for electricity generated from biomass, incentivizing its production.
- Tax credits and grants: Financial incentives, such as tax credits and grants, can help reduce the costs of biomass energy projects.
Can biomass energy provide electricity for remote areas?
Yes, biomass energy can be an excellent solution for providing electricity in remote areas:
- Off-grid systems: Biomass power plants or small-scale gasifiers can be implemented in areas where grid connections are not feasible.
- Local resource utilization: Biomass energy utilizes locally available resources, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
- Rural electrification: Biomass energy projects can support rural electrification efforts, bringing power to underserved communities.
Are there any environmental concerns associated with biomass energy?
While biomass energy is considered a renewable and lower-carbon option, there are some environmental concerns to consider:
- Land use change: The cultivation of energy crops for biomass production can lead to deforestation, habitat loss, and conversion of agricultural land.
- Water consumption: Certain biomass conversion processes, like corn ethanol production, can have high water requirements, potentially impacting local water resources.
- Air pollution: Inefficient biomass combustion or inadequate emission control systems can result in air pollution, although modern technologies are improving these aspects.
What are the potential future advancements in biomass energy?
Future advancements in biomass energy may include:
- Advanced conversion technologies: Continued research and development can lead to more efficient and cleaner biomass conversion processes.
- Biochemical conversion: Advancements in biochemical processes can enable the production of valuable chemicals and materials from biomass.
- Second-generation feedstocks: Exploring non-food crops and agricultural residues as feedstocks can reduce competition with food production.
- Integrated systems: Integrating biomass energy with other renewable energy sources, like solar or wind, can create more reliable and sustainable energy systems.
In conclusion, biomass energy is a renewable energy source derived from organic matter. It offers various benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, waste management, and local economic development. However, challenges such as resource availability, high capital costs, and environmental impacts need to be considered. Biomass energy can contribute to mitigating climate change and can be sustained through regulated harvesting, efficient use, carbon neutrality, and environmental considerations. While biomass energy has advantages over other renewables in terms of reliability and infrastructure, it also has limitations in resource availability and emissions. Policies and incentives exist to support biomass energy development, and it can provide electricity for remote areas. Environmental concerns such as land use change, water consumption, and air pollution should be addressed. Future advancements may include advanced conversion technologies, biochemical processes, alternative feedstocks, and integrated energy systems.