what is biomass energy simple definition
What Is Biomass Energy?
Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy derived from organic matter, such as plants, animal waste, and agricultural residues. It is a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy source that can be used for heating, electricity generation, and transportation fuels.

Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice
Biomass energy offers numerous advantages and should be considered as a top choice for meeting our energy needs. Here are some reasons why:
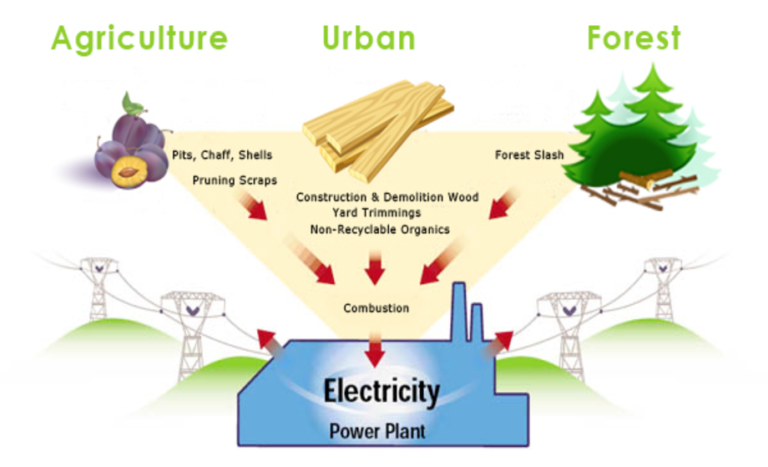
Most Asked Questions about Biomass Energy:
1. How does biomass energy work?
Biomass energy is produced through several processes, including:
- Burning organic materials
- Converting biomass into combustible gases
- Using biomass to produce liquid biofuels
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy works by harnessing the energy stored in organic matter. When biomass is burned, the heat energy released can be used to generate steam, which can power turbines and produce electricity. Biomass can also be converted into combustible gases, such as methane, through processes like anaerobic digestion. Additionally, biomass can be converted into liquid biofuels, such as biodiesel and ethanol, which can be used as replacements for fossil fuels.
2. What are the benefits of biomass energy?
The benefits of biomass energy include:
- Renewable and sustainable energy source
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Utilizes organic waste materials
- Creates jobs and economic opportunities
- Reduces dependency on fossil fuels
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy is a renewable and sustainable energy source because organic materials can be continuously replenished. By using biomass instead of fossil fuels, the generation of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, is reduced, mitigating climate change. Biomass energy also provides a solution for the management of organic waste materials, as it enables their conversion into useful energy. The production and utilization of biomass energy can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs and opportunities in the agricultural and energy sectors. Moreover, by reducing dependence on fossil fuels, biomass energy enhances energy security and reduces the vulnerability of countries to fluctuations in oil prices.
3. What are some examples of biomass energy?
Examples of biomass energy sources include:
- Wood and wood pellets
- Agricultural crops and residues
- Animal waste
- Algae
- Landfill gas
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy can be derived from a variety of organic sources. Wood and wood pellets are commonly used as biomass fuel for heating and electricity generation. Agricultural crops and residues, such as corn stalks and sugarcane bagasse, can be converted into biomass energy through processes like combustion or gasification. Animal waste, such as manure, can be utilized for biogas production through anaerobic digestion. Algae can be cultivated and converted into biofuels, such as biodiesel. Landfill gas, which is produced by the decomposition of organic waste in landfills, can also be captured and used as a source of biomass energy.
4. Is biomass energy sustainable?
Yes, biomass energy is considered sustainable. Unlike fossil fuels that deplete finite resources, biomass can be continuously replenished through responsible management of organic materials.
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy is sustainable because the organic materials used to produce it can be grown and replenished. Responsible management practices, such as reforestation and proper waste management, ensure a continuous supply of biomass feedstocks. Additionally, the use of biomass energy contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and helps mitigate climate change, further enhancing its sustainability.
5. How does biomass energy compare to fossil fuels?
Biomass energy has several advantages over fossil fuels:
- Biomass is a renewable energy source, while fossil fuels are finite resources.
- Biomass energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions, while fossil fuels contribute to climate change.
- Biomass utilizes organic waste materials, while fossil fuels require extraction and refining.
Expert Explanation:
In comparison to fossil fuels, biomass energy offers key advantages. Biomass is considered a renewable energy source because it can be continuously grown and replenished, whereas fossil fuels are finite resources that take millions of years to form. The combustion of biomass releases carbon dioxide, but since the carbon in biomass was recently absorbed from the atmosphere during plant growth, it does not contribute to a net increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. In contrast, the burning of fossil fuels releases carbon that has been trapped underground for millions of years, significantly increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and contributing to climate change. Furthermore, biomass energy utilizes organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues and animal waste, which would otherwise contribute to environmental problems if not properly managed. In contrast, the extraction and refining of fossil fuels cause significant environmental and ecological damage.
6. How does biomass energy impact the environment?
Biomass energy has both positive and negative environmental impacts:
- Positive impacts include reduced greenhouse gas emissions and utilization of organic waste materials.
- Negative impacts include air pollution and land use concerns.
Expert Explanation:
The positive environmental impacts of biomass energy include reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, as biomass fuel combustion produces carbon dioxide that is part of the natural carbon cycle. Biomass energy also enables the utilization of organic waste materials, reducing their negative environmental impact. However, the combustion of biomass can release air pollutants, such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which contribute to air pollution and can have adverse health effects. Additionally, large-scale biomass production may require significant land use, which can raise concerns about deforestation, habitat loss, and competition with food crops.
7. Can biomass energy be used for transportation?
Yes, biomass energy can be converted into biofuels that can be used in transportation.
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy can be converted into biofuels, such as biodiesel and ethanol, which can be used as alternatives to traditional fossil fuels in transportation. Biodiesel is typically produced from vegetable oils or animal fats through a process called transesterification. Ethanol, on the other hand, is commonly produced through the fermentation of sugars derived from biomass feedstocks, such as corn or sugarcane. These biofuels can be used in various forms, such as blending biodiesel with diesel fuel or using ethanol as a gasoline additive.
8. Is biomass energy economically viable?
Yes, biomass energy can be economically viable, especially in regions with abundant biomass resources and supportive policies.
Expert Explanation:
The economic viability of biomass energy depends on several factors, including the availability and cost of biomass feedstocks, the efficiency of conversion technologies, and government incentives and policies. In regions with ample biomass resources, such as agricultural areas or forestry regions, biomass energy can be a cost-effective option. Additionally, supportive policies, such as renewable energy targets, tax credits, and feed-in tariffs, can make biomass energy more economically competitive with fossil fuels.
9. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The future outlook for biomass energy is promising, as it plays a crucial role in transitioning to a low-carbon and sustainable energy system.
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy is expected to continue to grow in importance as countries strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy systems. The development of advanced biomass conversion technologies, such as advanced gasification and pyrolysis, can improve the efficiency and environmental performance of biomass energy. Additionally, the use of biomass as a feedstock for the production of biofuels, including advanced biofuels, holds promise for decarbonizing the transportation sector. However, the sustainable and responsible sourcing of biomass feedstocks, as well as addressing the potential environmental and social impacts associated with large-scale biomass production, will be critical for the future success of biomass energy.
10. How does biomass energy contribute to rural development?
Biomass energy can contribute to rural development in several ways:
- Creation of job opportunities in biomass production and processing
- Increased income for farmers and rural communities
- Reduction of energy costs
Expert Explanation:
Biomass energy can have a positive impact on rural development by creating job opportunities in biomass production, harvesting, and processing. This can benefit rural communities by providing employment opportunities and stimulating economic growth. Additionally, biomass energy can offer income diversification for farmers, who can grow dedicated energy crops or sell biomass feedstocks. The use of biomass energy can also help reduce energy costs for rural households and businesses, as locally produced biomass can replace more expensive imported fossil fuels.
11. Are there any challenges associated with biomass energy?
Yes, there are several challenges associated with biomass energy:
- Availability and sustainability of biomass feedstocks
- Efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass conversion technologies
- Environmental and social impacts of large-scale biomass production
- Policy and regulatory uncertainties
Expert Explanation:
One of the key challenges of biomass energy is ensuring the availability and sustainability of biomass feedstocks. This includes responsible sourcing of biomass to avoid deforestation and negative impacts on biodiversity. The efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass conversion technologies also present challenges, as improving the efficiency and reducing the costs of biomass energy production are essential for its widespread adoption. Large-scale biomass production may raise concerns about land use change, habitat loss, and competition with food crops, highlighting the importance of sustainable biomass production practices. Furthermore, policy and regulatory uncertainties, such as changing government incentives and support mechanisms, can create challenges for biomass energy project developers and investors.
12. What are the current innovations and research in biomass energy?
Current innovations and research in biomass energy focus on:
- Advanced biomass conversion technologies
- Development of sustainable biomass feedstocks
- Integration of biomass with other renewable energy sources
Expert Explanation:
Researchers and innovators are working on developing advanced biomass conversion technologies that can improve the efficiency, environmental performance, and cost-effectiveness of biomass energy. This includes advancements in gasification, pyrolysis, and biomass-to-liquid conversion processes. The development of sustainable biomass feedstocks, such as energy crops with high yields and low environmental impacts, is another area of active research. Additionally, there is growing interest in integrating biomass with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to create hybrid energy systems that can provide reliable and sustainable power.
Overall, biomass energy offers a renewable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly option for meeting our energy needs. It has numerous advantages and applications, ranging from heating and electricity generation to transportation fuels. However, it also presents challenges that need to be addressed, such as ensuring the sustainability of biomass feedstocks and improving the efficiency of biomass conversion technologies. With continued research, innovation, and supportive policies, biomass energy can play a significant role in our transition to a low-carbon and sustainable energy future.