what is the environmental impact of biomass energy
Article Title: The Negative Environmental Impacts of Biomass Energy
1. What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy that is derived from organic matter, such as plants and agricultural waste. It involves converting these materials into usable energy sources, including heat, electricity, and biofuels.
2. How does biomass energy contribute to renewable energy goals?
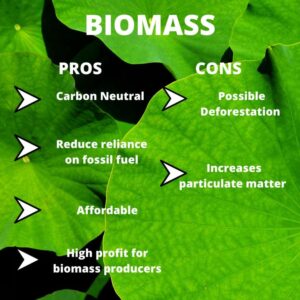
Biomass energy is considered a renewable energy source because the plants used for biomass can be regrown and carbon dioxide emissions from biomass combustion can be offset by replanting. Biomass has the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
3. What are the negative environmental impacts of biomass energy?
Biomass energy, despite its renewable nature, can still have negative environmental impacts:
- Deforestation and habitat destruction: Large-scale biomass production may require clearing land, leading to deforestation and the loss of valuable ecosystems.
- Air pollution: Some biomass energy processes produce harmful pollutants, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide. These pollutants can contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Water usage and contamination: Biomass energy production can require significant amounts of water, potentially leading to water scarcity issues. It can also result in the release of pollutants into water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
- Transportation and emissions: Biomass materials often need to be transported over long distances, increasing carbon emissions from transportation vehicles.
4. Can biomass have a part to play in a renewable future?
While biomass energy has its drawbacks, it can still play a role in a renewable future, but careful consideration and management are essential. Here are some points to consider:
- Biomass can provide a reliable and readily available source of energy, especially in regions with abundant organic waste.
- Improved biomass technologies and practices can help minimize negative environmental impacts and enhance the efficiency of energy conversion processes.
- Utilizing crop residues and agricultural waste as biomass can help reduce waste and provide additional revenue streams for farmers.
- Combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, biomass energy can potentially become carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative.

5. Are there any alternatives to biomass energy?
Yes, there are several alternatives to biomass energy that can also contribute to renewable goals:
- Solar power: Harnessing energy from the sun through solar panels or solar thermal systems.
- Wind power: Utilizing wind turbines to convert wind energy into electricity.
- Hydroelectric power: Generating electricity through the flow of water in rivers or dams.
- Geothermal energy: Tapping into the Earth's internal heat to produce electricity or generate heat.
6. How does biomass energy compare to fossil fuels in terms of emissions?
When properly managed, biomass energy can have lower net carbon emissions compared to fossil fuels. Since biomass comes from recently living plants, the carbon released during its combustion is part of the natural carbon cycle. In contrast, fossil fuels release carbon that has been sequestered for millions of years, leading to a net increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
7. Is biomass energy economically viable?
The economic viability of biomass energy depends on various factors, including feedstock availability, government incentives, technological advancements, and energy prices. In some cases, biomass energy can be cost-competitive with fossil fuels, especially when combined with other revenue streams like selling by-products. However, the economics can vary significantly depending on regional conditions and the scale of biomass production.
8. Can biomass energy be used in residential settings?
Yes, biomass energy can be used in residential settings for heating and electricity generation. Examples include wood pellets, agricultural residues, and biogas produced from organic waste. However, it is important to consider and address the environmental and health impacts associated with biomass combustion, such as emissions and air quality concerns.
9. What are the potential health risks associated with biomass energy?
Exposure to pollutants released during biomass combustion can pose health risks, especially for individuals living in close proximity to biomass power plants or using biomass for heating. Health effects may include respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and increased susceptibility to infections. Proper monitoring, emission controls, and adherence to health and safety regulations are crucial for minimizing these risks.
10. How can the negative environmental impacts of biomass energy be mitigated?
Several measures can be implemented to mitigate the negative environmental impacts of biomass energy:
- Promoting sustainable biomass sourcing, including using residues and waste materials instead of dedicated feedstocks.
- Implementing advanced air pollution control technologies to minimize the release of harmful pollutants.
- Investing in research and development for more efficient biomass conversion processes.
- Encouraging the use of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to reduce net carbon emissions.
- Enhancing water conservation and management practices within biomass production and processing.
11. What role does government policy play in the development of biomass energy?
Government policies and regulations can significantly influence the development and adoption of biomass energy:
- Subsidies and incentives can encourage investment in biomass energy infrastructure and technological advancements.
- Renewable energy targets and mandates can drive the expansion of biomass energy capacity.
- Emissions regulations can set limits on pollutants released during biomass combustion, promoting cleaner practices.
- Land use policies can guide sustainable biomass production, preventing deforestation and habitat destruction.
12. What are some successful case studies of biomass energy implementation?
There are several successful case studies showcasing the implementation of biomass energy:
- Sweden: Sweden has made significant progress in utilizing biomass for heat and electricity generation, with biomass accounting for a major share of the country's total energy consumption.
- United States: Many states in the U.S. have implemented biomass energy projects, particularly in the form of wood pellet production and utilization for residential heating.
- Finland: Finland has actively promoted the use of biomass in combined heat and power plants, contributing to the country's renewable energy targets and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Biomass energy, while having negative environmental impacts, has the potential to play a role in a renewable future. It can provide a reliable and abundant energy source, particularly in regions with ample biomass resources. However, careful management, technological advancements, and adherence to environmental and health regulations are necessary to mitigate the negative effects associated with biomass energy. Alongside other renewable energy sources, biomass can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a more sustainable energy system.